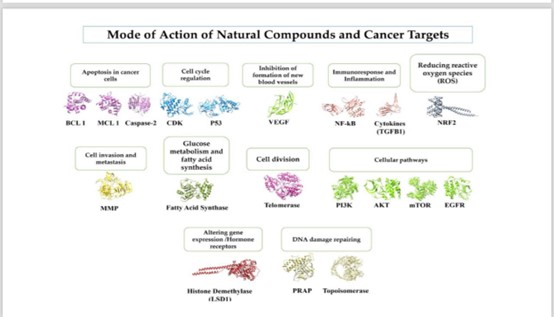
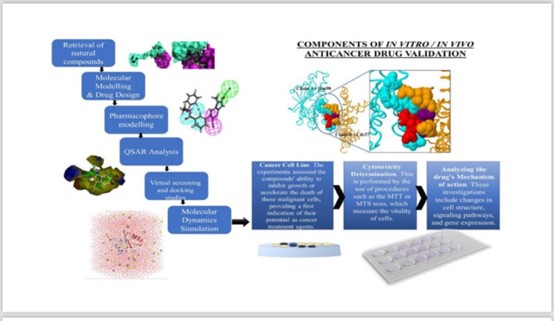
Under the supervision of the Dean of the College of Pharmacy, Associate Professor Dr. Sarmed H. Kathum Alkhateeb, the Continuing Education Unit, in cooperation with the Ibn Sina Unit at the University of Baghdad/College of Pharmacy, held an electronic workshop entitled “Some Active Substances Extracted from Natural Plants Used to Treat Certain Cancers,” delivered by Assistant Professor Dr. Amjad Haseb, a faculty member at the Pharmacognosy and Medical Plants Department. The workshop aimed to identify the most common types of cancer in the world, in women and men, as well as learn about the most important treatment methods used to treat cancer, including the use of certain active substances extracted from natural plants. The workshop included several topics, including an introduction to cancer, the most widespread cancer in the world, which has been identified as breast cancer, colon cancer, and lung cancer. The workshop also included an explanation of treatment methods used for various types of cancer, such as surgery therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, gene therapy, stem cell use, etc. One of these methods is the use of active substances extracted from natural plants in certain cancer cases. The benefits and disadvantages of the use of active substances extracted from natural plants have also been identified in terms of the identification of active substances found in plants, methods of isolating these substances, and other challenges. The mechanisms of action of these active substances have also been identified, either by regulating the cell life cycle or by inhibiting new blood vessel formation and other methods. For example, mistletoe herb is used to treat some types of cancer by stimulating apoptosis of the cancer cell, destroying the cell membrane, and hence causing the death of the cancer cell. The workshop concluded to enhance awareness of increasing attention towards the use of these active substances, as in many countries these active substances are used in combination with chemotherapy or other treatment methods to be more effective and have fewer adverse effects on the patient.