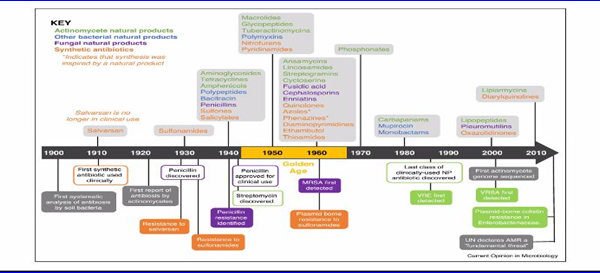
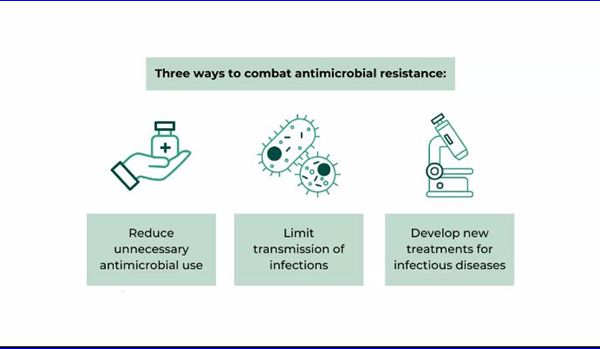
Under the supervision of the Dean of the College of Pharmacy, Associate Professor Dr. Sarmed H. Kathum Alkhateeb, the Continuing Education Unit, in collaboration with Ibn Sina Unit for Electronic Education at the University of Baghdad/College of Pharmacy, held an electronic workshop entitled (New Natural Products to Meet the Antibiotic Crisis, delivered by Assistant Professor Dr. Amjad Hasib, a faculty member at the Pharmacognosy and Medicinal Plant Department. The workshop aimed to identify the most important natural sources used as antibiotics. The workshop included several topics, including the history of antibiotic exploration, whether from natural or manufactured sources, such as the group actinomycetes, which includes lincosamides, chloramphenicol, macrolides, etc., are natural sources first discovered in 1920. There is a group of antibiotics detected by bacteria that are between monobactam and polymyxins, and others that were discovered between 1940 and 1980; others are from fungi such as pencillins. For example, pencillins were first discovered in 1930, followed by manufactured sources such as azoles, sulfonamides, and salvarsan, which was the first synthetic antibiotic discovered in 1910. Antibiotic resistance is considered a common problem globally and causes a lot of deaths. In the UK, research was done in 2016; this research estimates that the number of deaths in 2050 due to antibiotic resistance will reach 10 million. A study of 204 countries was carried out. Iraq represents a level of 80 out of 204 countries in terms of antibiotic resistance. In the Middle East and North Africa, Iraq occupies the ninth position out of 21 countries. Deaths as a result of antibiotic resistance in Iraq are the highest number of deaths compared to suicides or deaths as a result of psychiatric and other illnesses. The causes of resistance are the intense and incorrect use of antibiotics, and therefore, how to reduce antibiotic resistance has been identified by the correct use of treatment, reducing the spread of infectious diseases by taking vaccines regularly, and detecting new antibiotics that will be effective. The workshop concluded that work must be done to discover modern natural sources that can act as antibiotics in order to reduce resistance and decrease infectious diseases.